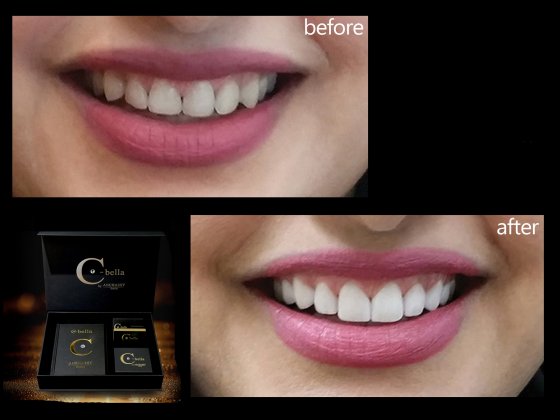
Uneven gums or too much gum showing when speaking or smiling (gummy smile) can affect the smile and look unsightly. Gum correction is to reshape the gums to reduce the amount of gums visible on either a single tooth/ area or on multiple teeth/ areas. This is especially useful when trying to create a symmetrical outline of the gum.
Gum contouring alone is considered a cosmetic procedure and as part of other necessary periodontal procedures, such as crown lengthening, pocket reduction, and regenerative procedures.
Crown lengthening is a surgical procedure to expose a greater amount of tooth structure for the purpose restoring the tooth prosthetically. This is done by incising the gingival tissue around a tooth and, after temporarily displacing the soft tissue, removing a given height of alveolar bone from the circumference of the tooth or teeth being operated on.During the dental crown lengthening procedure, excess gum and bone tissue is reshaped to expose more of the natural tooth. This can be done to one tooth, to even your gum line, or to several teeth to expose a natural, broad smile.
Purpose of crown lengthening is to make a restorative or cosmetic dental procedure possible by adjusting the gum and bone level to expose more of the tooth so it can be restored.
Gingivitis ("inflammation of the gum tissue") is a non-destructive disease that occurs around the teeth. The most common form of gingivitis is in response to bacterial biofilms (also called plaque) that is attached to tooth surfaces, termed plaque-induced gingivitis.
Gingivitis is reversible with good oral hygiene; however, without treatment, gingivitis can progress to periodontitis, in which the inflammation of the gingiva results in tissue destruction and bone resorption around the teeth.
Gingivitis can be prevented through regular oral hygiene that includes daily brushing and flossing and removing of the plaque by scaling and polishing done in dental office.
Periodontitis, is known as gum disease is a set of inflammatory diseases affecting the tissues surrounding the teeth. Periodontitis involves progressive loss of the alveolar bone around the teeth, and if left untreated, can lead to the loosening and subsequent loss of teeth.
Periodontitis is caused by microorganisms that adhere to and grow on the tooth's surfaces, along with an over-aggressive immune response against these microorganisms. A diagnosis of periodontitis is established by inspecting the soft gum tissues around the teeth with a probe (a clinical examination) and by evaluating the patient's X-ray films (radiographic examination), to determine the amount of bone loss around the teeth.
The first step of successful periodontal treatment is establishing good oral hygiene and removal of microbial plaque and calculus called scaling and debridement that will be done by the dentist.